Introduction
IPTV offers viewers more flexibility and control over their viewing experience. But how exactly does IPTV work? Let’s explore the guide provides a simple, beginner-friendly explanation of the key components and processes involved in delivering IPTV services to your television.
What is IPTV?
IPTV refers to a system where television content is delivered to consumers over Internet Protocol (IP) networks using broadband connections. Instead of relying on radio frequency signals transmitted through cables or satellites like traditional TV services, IPTV uses the internet infrastructure to stream video content to users.
Some key characteristics of IPTV include:
- Delivers high-quality video and audio streams over IP networks
- Supports live TV, video on demand (VOD), and time-shifted services
- Provides an interactive viewing experience with advanced features
- Allows personalized content recommendations and schedules
- Enables multi-screen delivery to various devices
How IPTV Works
The fundamental principle of IPTV is the use of internet protocols to transmit TV signals. This process involves four main steps:
- Content Acquisition: TV channels and programs are obtained from various sources like over-the-air broadcasts, cable feeds, or media production houses.
- Encoding: The video content is digitized and encoded into formats like MPEG-2, MPEG-4, or H.264 using video encoders.
- Compression: Advanced compression techniques are applied to reduce bandwidth usage.
- Storage: The encoded and compressed content is stored on the IPTV service provider’s servers or a content delivery network (CDN).
- Delivery: When a user requests content, it is retrieved from the servers and delivered over the IP network using protocols like IP Multicast or HTTP.
- Reception: The user receives the IPTV streams on their connected device like a smart TV or set-top box, which decodes and displays the content.
IPTV Services
IPTV offers a wide range of television services and interactive features:
- Live TV: Watch real-time broadcasts of TV channels just like traditional cable or satellite.
- Video on Demand (VOD): Stream movies and shows from an on-demand library at any time.
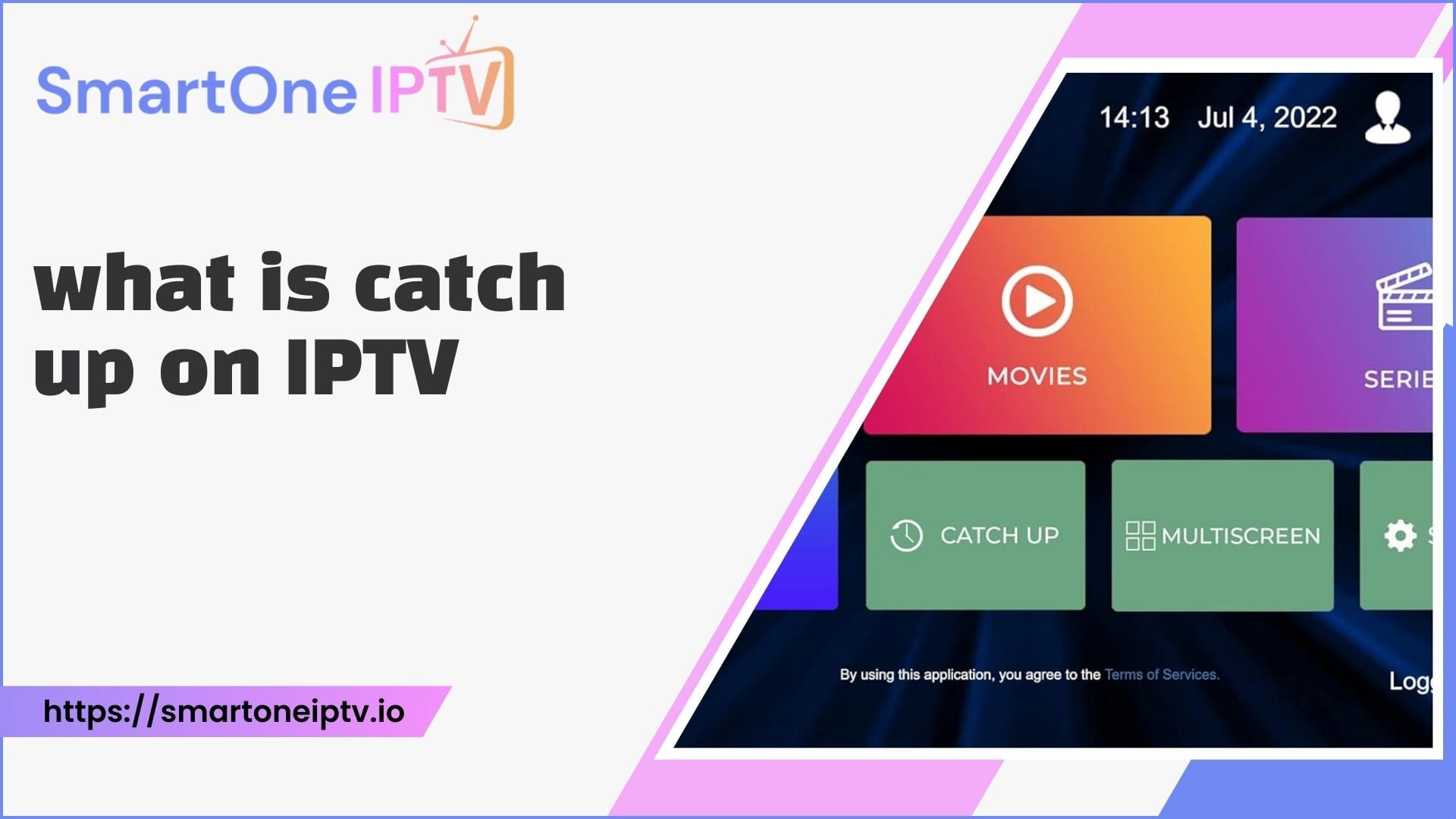
- Time-Shifted TV: Pause, rewind, and replay live programming using network DVR capabilities.
- Start Over: Restart a live show from the beginning even after it has started.
- Interactive Program Guide: Navigate channels and programming using an interactive guide.
- Parental Controls: Manage access to age-restricted content.
- Multi-View: Watch multiple channels simultaneously on a single screen.
Key Components of an IPTV System
An end-to-end IPTV infrastructure consists of:
- Headend: Where content is acquired, encoded, and streamed to the service provider’s network.
- Middleware: Manages subscriber accounts, content delivery, and interactivity.
- Distribution Network: Transports video traffic between the provider and consumers, usually via a high-speed broadband connection.
- Set-Top Box (STB): Decodes and displays IPTV streams on traditional televisions.
- Residential Gateway: Router that connects the home network and STB to the operator’s network.
Technical Requirements for IPTV
To enjoy IPTV, certain technical standards must be met:
- Internet Speed: A minimum speed of 25 Mbps is recommended for HD content, with higher speeds required for 4K streaming.
- Compatible Devices: Devices like the Amazon Fire TV Stick or NVIDIA SHIELD offer excellent performance for IPTV streaming.
- IPTV Service Subscription: Choosing the right service involves considering factors such as content library, streaming quality, and device compatibility.
- IPTV Applications: Apps like TiviMate and IPTV Smarters provide intuitive interfaces and enhanced streaming experiences.
Common Protocols Used in IPTV
IPTV uses several protocols to ensure smooth and efficient streaming:
- RTSP: Manages real-time streaming sessions.
- IGMP: Facilitates multicast group management, essential for live TV.
- HTTP: Supports adaptive bitrate streaming, adjusting video quality based on network conditions.
- UDP and TCP: Ensure data packets are transmitted reliably and quickly.
What Do You Need to Set Up IPTV on Your TV?
To start streaming IPTV, you’ll need:
- High-Speed Internet Connection: Minimum speeds of 25 Mbps for HD and 50 Mbps for 4K are recommended.
- Smart TV or IPTV Box: A smart TV with built-in IPTV capabilities or an external streaming box or stick.
- IPTV Subscription: Sign up for a paid IPTV service from a provider.
- IPTV App: Download the provider’s app on your device or use a third-party IPTV player app.
- Router Setup: You may need to configure router settings and ports for IPTV functionality.
- Cables and Connections: HDMI cables are needed to connect devices to your TV.
- VPN (Optional but Recommended): A VPN enhances privacy and security and may help bypass geographical restrictions.
How IPTV Set-Top Boxes Work with Televisions
An IPTV set-top box is a device that connects to the internet and receives IPTV signals from an IPTV service provider. It then decodes those signals and outputs video content to a TV in a compatible format. Key components of an IPTV STB include:
- Processor – Decodes video signals and runs the STB’s operating system.
- Memory – Stores channel info, user settings, etc.
- Storage – Some models have hard drives for recording shows.
- Operating System – Manages the STB’s functions and runs IPTV apps.
- Outputs – HDMI, analog AV, and optical audio ports to connect to a TV.
- Networking – Ethernet and/or WiFi to connect to the internet.
Network Connectivity
An IPTV STB must connect to the internet to receive IPTV streams. This is done via:
- Wired Ethernet – Provides the most stable and highest speed connection.
- WiFi – Allows flexible placement, but may be less reliable. Newer boxes support the latest standards like 802.11ac.
- Hybrid – Some STBs have both Ethernet and WiFi for maximum flexibility.
A stable, high-speed network connection is crucial for smooth IPTV streaming, especially for HD and 4K content.
Signal Reception and Decoding
The IPTV STB receives IPTV streams over the internet using IP protocols. The video signals are encoded in formats like MPEG-2, H.264, HEVC, etc. The STB’s processor runs software to:
- Decode the incoming video signals into viewable content.
- Decrypt encrypted streams using keys provided by the IPTV provider.
- Optimize streaming using adaptive bitrate technologies.
This process converts the IPTV streams into audio/video output compatible with the connected TV.
Content Delivery to the TV
The decoded IPTV content is sent from the STB to the TV via:
- HDMI – Digital audio/video interface that supports up to 4K resolution. Provides the best quality.
- AV/Component cables – Analog interface for older TVs. Limited to 720p or 1080i resolution.
- Optical Audio – For connecting to external audio systems.
The video is output at the TV’s native resolution. Advanced STBs can upscale lower-resolution streams.
User Interface and Features
The IPTV STB provides an interface for selecting channels, accessing VOD content, and configuring settings. Key interface features include:
- Electronic Program Guide (EPG)
- Video on Demand access
- Search and recommendations
- Customizable channel lists
- Parental controls
- Closed captioning support
Many STBs also offer features like:
- Recording via internal DVR or cloud DVR
- Streaming media apps like Netflix, Hulu, etc.
- Multi-room viewing on other STBs
- Smart home device integration
Advantages and Disadvantages of IPTV
Advantages
- Flexibility and Convenience: IPTV allows viewers to watch their favorite content anytime, anywhere.
- Interactivity: Interactive features enhance user engagement.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often cheaper than traditional cable, with the option to pay for only desired content.
- Quality and Resolution: Supports high-quality streaming, including 4K and HDR content.
Disadvantages
- Internet Dependency: A stable, high-speed internet connection is essential.
- Latency Issues: Live streams may experience slight delays.
- Bandwidth Consumption: Heavy streaming can strain internet bandwidth.
- Security Concerns: Risks of cyber attacks and privacy issues.
The Future of IPTV
Some exciting innovations on the horizon include:
- UHD, 4K, and 8K ultra high-definition TV support.
- Integration with virtual reality and augmented reality.
- Advanced personalization and recommendations through AI.
- Targeted advertising capabilities.
- Expanded device support including game consoles.
- 5G and edge computing integration for lower latency and enhanced mobility.
Conclusion
IPTV delivers live, on-demand, and time-shifted TV services with greater personalization and interactivity compared to traditional television. With its rising popularity across the world, IPTV promises to further enhance our television viewing experience as the technology evolves.